
- Electromagnetic radiant energy examples free#
- Electromagnetic radiant energy examples windows#
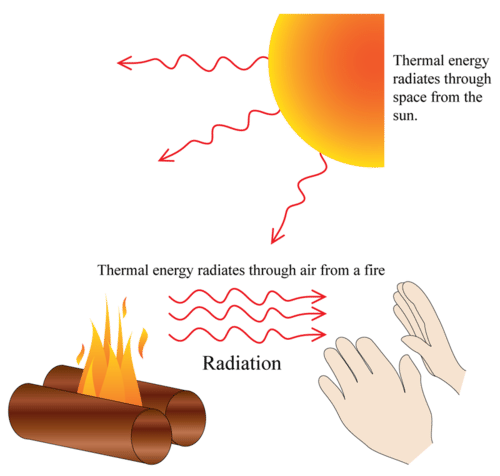
Light energy is radiant energy that the human eye can see.The entire distribution of electromagnetic radiation defined by frequency or wavelength is known as the electromagnetic spectrum.
Electromagnetic radiant energy examples free#
Get your free quotes today! Complete our quick quiz, and you’ll be contacted shortly.

Use our free solar quote system to get up to 3 free solar quotes from our network of trusted, local installers. Because Australia is located in the southern hemisphere, it receives sunlight primarily directed northward.
Electromagnetic radiant energy examples windows#
So your home generates more radiant heat from windows that face north. The sun rises in Australia at an angle towards the north facing aspect. While the amount of solar radiation, or electromagnetic energy, that is received at a specific location on the earth’s surface is known as solar insolation. The solar radiance is the kilowatts per square metre instantaneous power density.

Solar radiance and solar insolation are the two commonly used measurements to describe solar radiation. The amount of sunlight at a specific location at a particular time is a key point when designing solar PV systems. Technology transforms solar radiation into several types of energy, including heat and electricity.
Radiant energy (light) is required for human vision to see.Īny radiant energy from the sun is referred to as solar radiation. There are several ways to apply radiant energy: The solar constant varies by +/-3% because of the Earth’s slightly elliptical orbit around the Sun. The solar constant, roughly 1370 watts per square metre (W/m2), measures the sun’s strength per square metre on earth. Radiant energy from a radioactive source is used by radioisotope thermal generators to generate heat or electricity.ĭiscussing radiant energy collection typically refers to the power of sunlight passing through a square metre when facing the sun directly, and the earth is at its distance from the sun. Plant biomass can also be utilised to make biofuels. Animals can consume plants or animals that have recently consumed other animals or plants to receive some of this chemical energy as food. They take in solar radiation and convert it into chemical energy stored in molecules within their cells. Photosynthesis is the process through which plants capture and utilise light energy. Solar energy converts the radiant energy in the sun’s light into electricity. The usage of radiant energy collection includes: Less than 1% of this radiation is emitted in the radio, UV, and X-ray spectral bands. Microwaves, infrared light, ultraviolet light, X-rays, and gamma rays are the other radiant energy types that make up the electromagnetic spectrum. The range of all electromagnetic (EM) radiation or radiant energy types is known as the electromagnetic spectrum. People can only see photons with an extremely narrow range of energy, known as visible light. Since photons are so tiny, the energy of light is commonly identified in electron volts. Light energy is a type of radiant energy found in an electromagnetic wave-a little “packet” of energy is carried by tiny particles, known as photons. Two examples of radiant energy are the warmth from a hot stove and the heat from direct sunshine. Radiant energy is the energy of electromagnetic waves. Radiant energy, also known as electromagnetic radiation (EMR), is energy transmitted without a mass movement.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
